
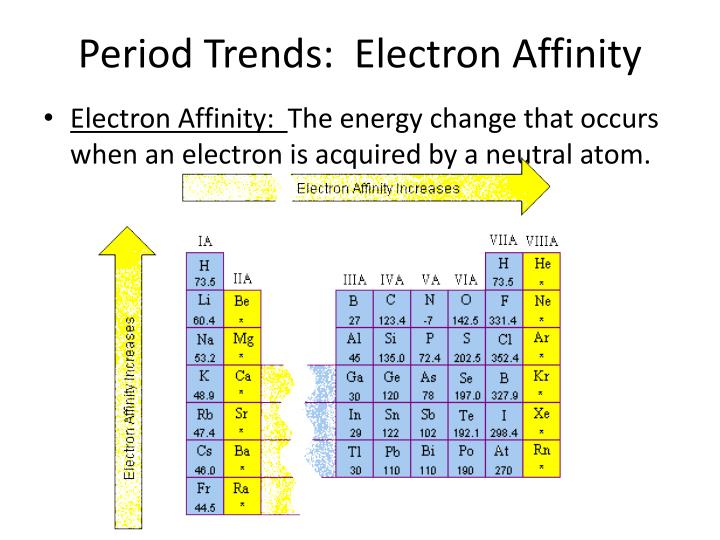
By convention, the negative sign shows a release of energy. This affinity is known as the first electron affinity, and these energies are negative. When an electron is added to a neutral atom, energy is released. To use electron affinities properly, it is essential to keep track of signs. Molecules with high electron affinity form very stable negative ions which are important in the chemical and health industry as they purify the air, lift mood, and most importantly, act as strong oxidizing agents. H + e – → H – – ∆H = Affinity = 72.8 kJ/molĮlectron affinity is one of the most important parameters that guide chemical reactivity. Electron affinities are more difficult to measure than ionization energies.Īn atom of Hydrogen in the gas phase, for example, gives off energy when it gains an electron to form an ion of Hydrogen.
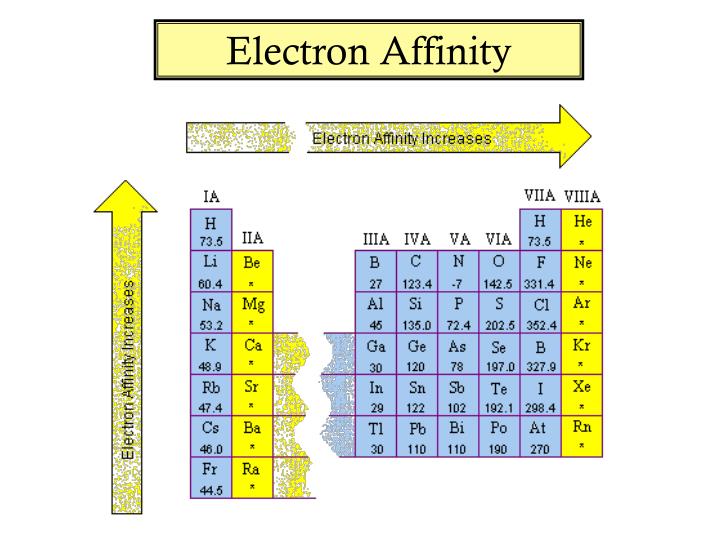
Note that ionization energies measure the tendency of a neutral atom to resist the loss of electrons. In other words, it can be expressed as the neutral atom’s likelihood of gaining an electron. The change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom or molecule (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion. In chemistry and atomic physics, the electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as: Electron Affinity and Electronegativity of HydrogenĮlectron Affinity of Hydrogen is 72.8 kJ/mol.įirst Ionization Energy of Hydrogen is 13.5984 eV.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
